Background#
I obtained a penetration testing tutorial from a public account, written by the expert micropoor. The original source (requires VPN): https://micropoor.blogspot.com/2019/01/php8.html
(Updated on 19-02-23) Micropoor also updates on Github, which is the most comprehensive source. You can use the script in this article to rename files while maintaining the order: https://github.com/Micropoor/Micro8. Soapffz has synchronized this project on Gitee, refer to this article: git clone too slow? Use Gitee as a proxy for elegant acceleration (turned into a water article due to failure)
You can directly use:
git clone https://gitee.com/soapffz/Micro8.git
Download, Micropoor is also updating on the Knownsec forum: https://www.kanxue.com/book-section_list-38.htm
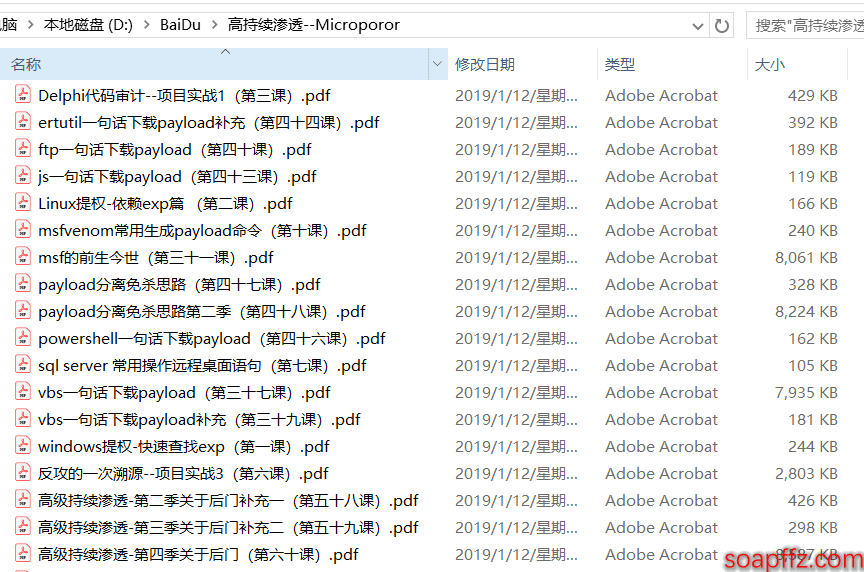
However, the file names are sorted as "Lesson xx", which is not convenient for sorting. So we are going to batch rename them like this:
For example, rename "msf 的前生今世(第三十一课).pdf" to "31-msf 的前生今世.pdf"
Code Implementation#
Extract Chinese Numerals for Sorting#
First, we need to extract the Chinese numerals for the lesson number using the re regular expression library:
import re
cc = 'msf的前生今世(第三十一课).pdf'
r1 = re.compile(u'[一二三四五六七八九十]{1,}')
print(r1.findall(cc))

As you can see, the Chinese numerals have been extracted.
Extract Lesson Names#
Reference link: https://www.cnblogs.com/lzhc/p/8744299.html
We need to extract the part of the lesson name that does not include the Chinese numerals for sorting, which means removing the text inside the parentheses:
import re
cc = 'msf 的前生今世(第三十一课).pdf'
a = re.sub(u"\\(.\*?)","",cc)
print(a)
Output: msf的前生今世.pdf
Convert Chinese Numerals to Arabic Numerals#
Reference article: https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000013048884
Consider the following points:
- Zero serves as a placeholder in Chinese numeral strings and can be ignored during processing.
- The combination of "一十" is usually shortened to "十", which means that if there is no number before "十", it is considered as "一十".
- The numbers before the units "千" (thousand), "百" (hundred), and "十" (ten) are single digits.
- The numbers before the unit "万" (ten thousand) can be composed of (3).
- The numbers before the unit "亿" (hundred million) can be composed of (3), (4), and "亿" itself.
Code implementation:
digit = {'一': 1, '二': 2, '三': 3, '四': 4, '五': 5, '六': 6, '七': 7, '八': 8, '九': 9}
def \_trans(s):
num = 0
if s:
idx_q, idx_b, idx_s = s.find('千'), s.find('百'), s.find('十')
if idx_q != -1:
num += digit[s[idx_q - 1:idx_q]] * 1000
if idx_b != -1:
num += digit[s[idx_b - 1:idx_b]] * 100
if idx_s != -1: # Ignore "一" before "十"
num += digit.get(s[idx_s - 1:idx_s], 1) * 10
if s[-1] in digit:
num += digit[s[-1]]
return num
def trans(chn):
chn = chn.replace('零', '')
idx_y, idx_w = chn.rfind('亿'), chn.rfind('万')
if idx_w < idx_y:
idx_w = -1
num_y, num_w = 100000000, 10000
if idx_y != -1 and idx_w != -1:
return trans(chn[:idx_y]) * num_y + \_trans(chn[idx_y + 1:idx_w]) * num_w + \_trans(chn[idx_w + 1:])
elif idx_y != -1:
return trans(chn[:idx_y]) * num_y + \_trans(chn[idx_y + 1:])
elif idx_w != -1:
return \_trans(chn[:idx_w]) * num_w + \_trans(chn[idx_w + 1:])
return \_trans(chn)
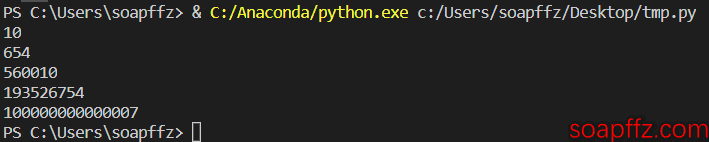
Testing:
print(trans('十'))
print(trans('六百五十四'))
print(trans('五十六万零一十'))
print(trans('一亿九千三百五十二万六千七百五十四'))
print(trans('一百万亿零七'))
Code Summary#
Reference article: https://www.cnblogs.com/kba977/p/3533367.html
# !/usr/bin/python
# - _ - coding:utf-8 - _ -
'''
@author: soapffz
@fucntion: Convert Chinese Numerals in File Names to Arabic Numerals
@Description: For example, rename "msf 的前生今世(第三十一课).pdf" to "31-msf 的前生今世.pdf"
@time: 2019-02-06
'''
import os
import re
digit = {'一': 1, '二': 2, '三': 3, '四': 4,
'五': 5, '六': 6, '七': 7, '八': 8, '九': 9}
def \_trans(s):
num = 0
if s:
idx_q, idx_b, idx_s = s.find('千'), s.find('百'), s.find('十')
if idx_q != -1:
num += digit[s[idx_q - 1:idx_q]] * 1000
if idx_b != -1:
num += digit[s[idx_b - 1:idx_b]] * 100
if idx_s != -1:
num += digit.get(s[idx_s - 1:idx_s], 1) * 10
if s[-1] in digit:
num += digit[s[-1]]
return num
def trans(chn):
chn = chn.replace('零', '')
idx_y, idx_w = chn.rfind('亿'), chn.rfind('万')
if idx_w < idx_y:
idx_w = -1
num_y, num_w = 100000000, 10000
if idx_y != -1 and idx_w != -1:
return trans(chn[:idx_y]) * num_y + \_trans(chn[idx_y + 1:idx_w]) * num_w + \_trans(chn[idx_w + 1:])
elif idx_y != -1:
return trans(chn[:idx_y]) * num_y + \_trans(chn[idx_y + 1:])
elif idx_w != -1:
return \_trans(chn[:idx_w]) * num_w + \_trans(chn[idx_w + 1:])
return \_trans(chn)
if __name__ == "__main__":
for filename in os.listdir("."): # print(filename)
split = filename.split(".") # Split the file name and extension
if split[1] == 'pdf':
name = re.sub(u"\\(.\*?)", "", filename) # Use regular expression to match the file name and Chinese numeral for sorting
cn_number = re.compile(u'[一二三四五六七八九十]{1,}').findall(filename)[-1::]
if cn_number: # To prevent manual conversion
number = trans(cn_number[0])
new_filename = str(number) + "-" + name # print(new_filename)
os.rename(filename, new_filename)
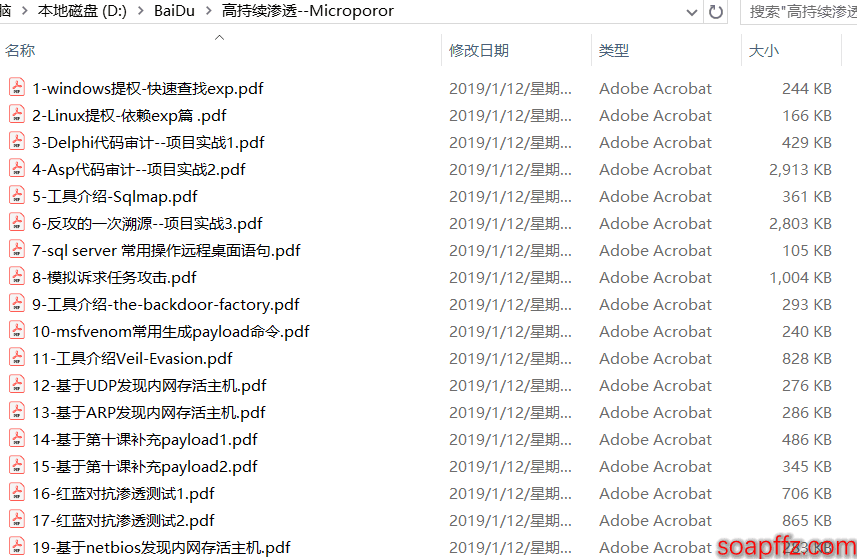
The result is as follows:
However, if you download the files directly from Micropoor's website or lsh4ck's website, the file names will be like this:
- 第一百课:HTTP 隧道 reDuh 第四季.pdf
- 第七十四课:基于白名单 regsvcs.exe 执行 payload 第四季.pdf
After testing, the above code does not consider Chinese numerals above one hundred. Modify the main function code as follows:
if __name__ == "__main__":
for filename in os.listdir("."): # print(filename)
portion = os.path.splitext(filename)
if portion[1] == '.pdf':
name = re.split(':', portion[0])[1]
cn_number = re.compile(
u'[一二三四五六七八九十零百千万亿]{2,}').findall(portion[0])[0]
if cn_number:
number = trans(cn_number)
new_filename = str(number) + "-" + (name) + ".pdf" # print(new_filename)
os.rename(filename, new_filename)
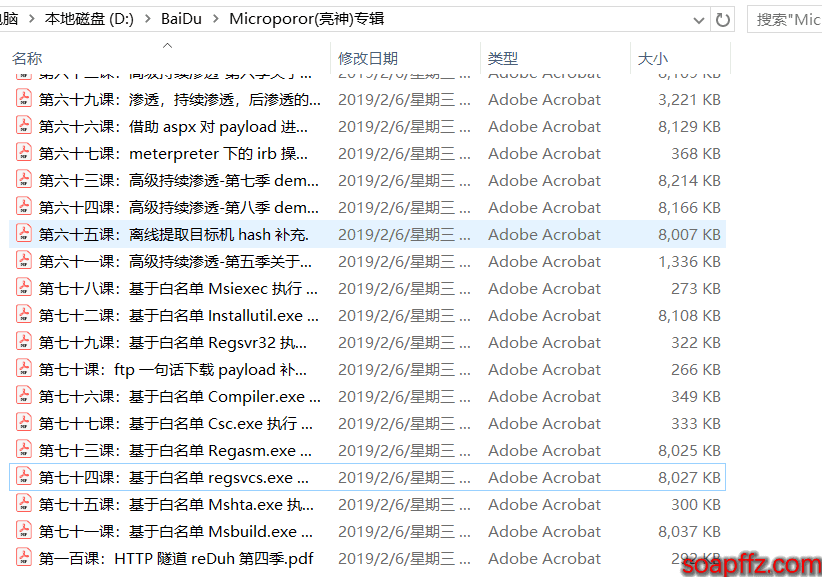
You can compare the two versions. Only a small part has been modified. The result is as follows:
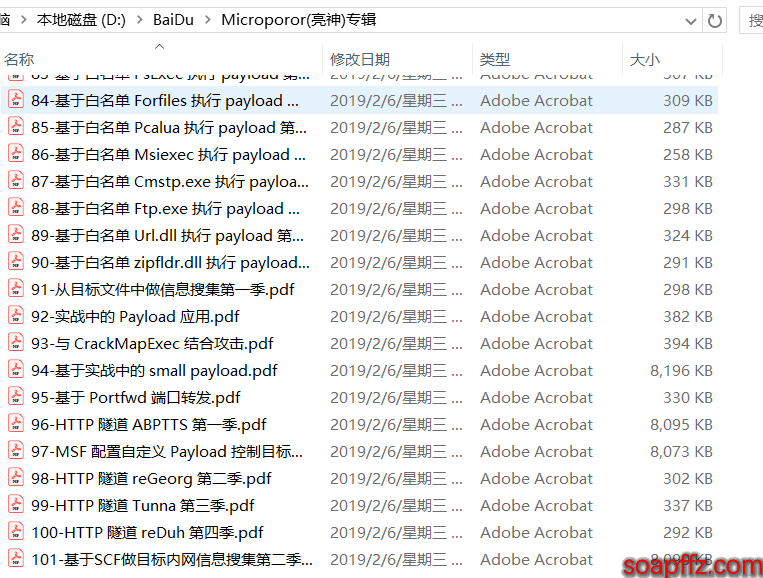
Do not execute the script with modified files and unmodified files together.