郑重声明: 此文章内分析用到的数据集仅为学习交流,本文未提供任何下载链接且已在 24 小时内删除,请勿用于非法用途否则产生的一切后果自行承担
tb#
事情起因#
代办事项之 - 整理手上的裤子之固定字符分割的 txt 导入 mysql 篇
txt 以四个减号----来分割邮箱和密码 (请忽略我的魔幻打码技术):
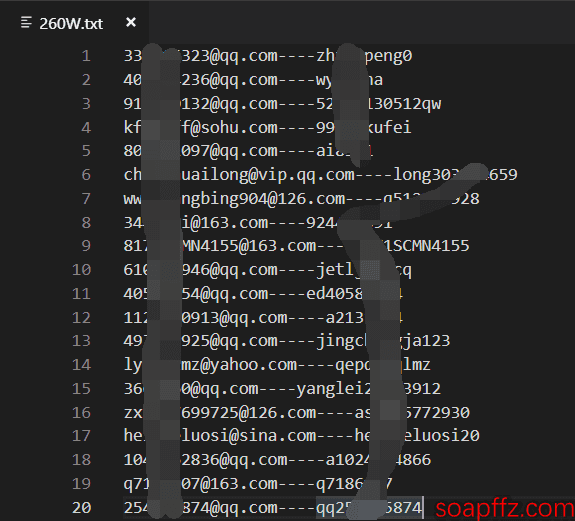
本篇文章就来试试用 Python 将这些固定字符分割的 txt 批量导入本地的mysql数据库
部分过程解释如下#
关于文件编码以及换行符#
文件编码#
当然是所有的工具和文件都是 utf8 编码的最好啦!
但是就像我刚才的这四个文本,下下来都是:
ASCII text, with CRLF line terminators
手动修改为 utf-8 是什么样子呢?
UTF-8 Unicode (with BOM) text, with CRLF line terminators
这两种平时是最经常看到的,啊?你问我为什么能在win用Linux的命令,因为我偶然发现git for windows里面提供了非常多的Linux命令,git for windows在你下Virtualbox的时候会提示你要不要安装,你也可以直接下载安装:传送门
建议没安的同学安一下,还是非常好用的 (这两家公司看到请给我打广告费谢谢),后面我们也要用到iconv、sed等Linux命令
使用file xxx.txt命令即可查看文件编码以及换行符
我们将ANSI编码的txt导入utf-8编码的数据库就报错了:
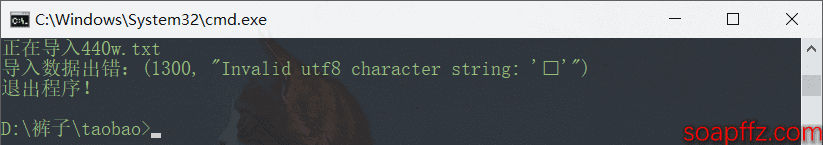
1300, "Invalid utf8 character string: '˹'"
我这里将所有的文件转换为UTF8编码的,先用前面说的命令行的file命令来试一下,这个秒出结果
Python中命令行语句的执行我们也在前面的文章《Python3 打印出电脑上所有 wifi 账号和密码》介绍过,我们这里直接上代码:
import os
txt_name_list = ['260W.txt','316W.txt','440W.txt','445W.txt',]
for i in txt_name_list:
print(os.popen('file {}'.format(i)).read())
效果如下:
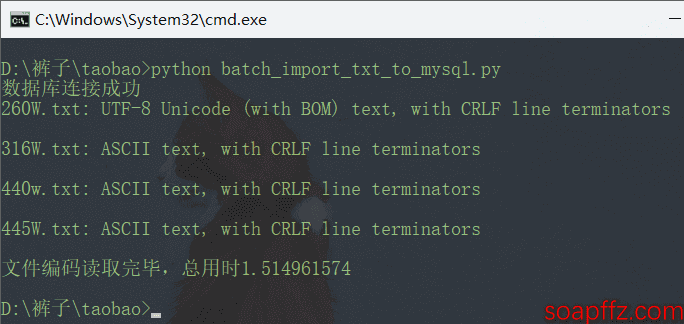
显示第一个为UTF-8,其他的为ANSI,但实际上我这里316W.txt也为UTF-8,可见file命令准确性不高
我们再试下 Python3 中的库chardet,参考文章:python 实现文本文件的编码检测和转换
for i in txt_name_list:
detector = UniversalDetector()
print("正在检测{}的文件编码".format(i))
detector.reset()
for line in open(i, 'rb').readlines():
detector.feed(line)
if detector.done:
break
detector.close()
print(detector.result)
大文件的检测真的是超慢,不过等待了很久之后还是能检测出316W.txt为UTF-8编码
我们改一下,将 readlines () 中加上参数1000000,发现检测不出来:
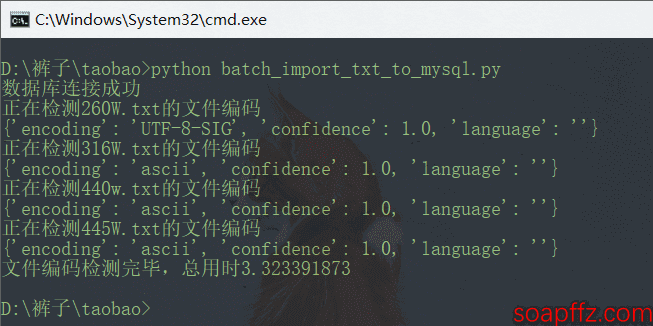
加到2000000行时又能检测出来:
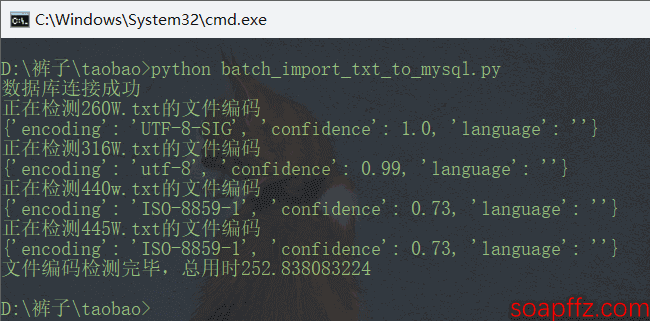
那我们就偷懒地以200W作为最大检测界限吧。
那么获得了文件的编码之后,我们判断其是否为utf8,不是的话将其使用命令iconv转换文件编码并重命名:
src_enc = detector.result['encoding']
# 如果编码不为utf-8,则用iconv将xx.txt转换为utf8-xx.txt
if 'utf-8' not in src_enc.lower():
utf8_txt_name = "utf8-{}".format(i)
print("{}不是utf-8编码,正在转换为{}".format(i, utf8_txt_name))
try:
os.popen(
'iconv -c -f {} -t utf-8 {} > {}'.format(src_enc, i, utf8_txt_name))
except Exception as e:
print("转换报错:{} \n 程序退出!".format(e))
exit(0)
processed_txt_filename_list.append(utf8_txt_name)
else:
processed_txt_filename_list.append(i)
换行符#
CRLF 代表回车换行,CR 回车,LF 换行,一般默认 CRLF 即可。CRLF 代表的就是 \n\r,这是 Windows 默认换行方式;LF 代表的就是 \r,这是 Unix 体系默认换行方式
Unix 体系下的文件在 Windows 里打开的话,所有文字会变成一行 (用 VSCODE 打开也能正常显示,VSC 看到请打钱谢谢);而 Windows 里的文件在 Unix 下打开的话,在每行的结尾可能会多出一个 ^M 符号。
那我就不改了,全部使用CRLF, 如果你要改也可以使用 sed 命令把所有可能存在的\n\r都换为\n
sed ’s/^M//’ filename > tmp_filename
其他方法参考文章:linux 去掉 windows 下文件中的 \r
pymysql 基本操作#
使用pymysql连接数据库并执行sql语句的基本用法如下:
# 连接数据库,密码后面可以加数据库名称
connect_mysql = pymysql.connect('localhost', 'root', 'root', charset='utf8')
# 得到一个可以执行SQL语句的光标对象,执行完毕返回的结果默认以元组显示
cursor = connect_mysql.cursor()
# 执行sql语句
cursor.execute('select * from `users`;')
# 关闭数据库连接
connect_mysql.close()
但是!在我使用pymysql.connect()函数连接数据库执行后面的加载文件导入命令load data local infile xxx.txt时,发现会报错:
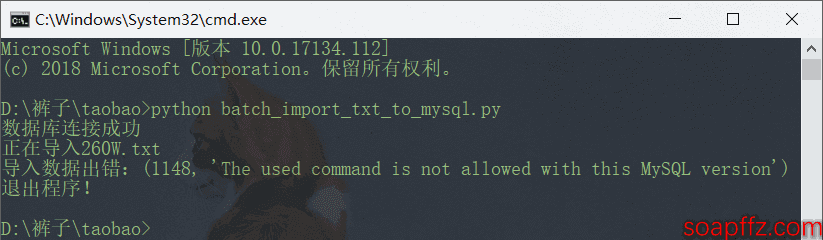
1148, 'The used command is not allowed with this MySQL version'
在网上查询说
出于安全考虑,默认是不允许从 client host 远程通过 load data 命令导数据的。
在这篇文章中找到了解决办法:
connect_mysql = pymysql.connections.Connection('localhost', 'root', 'root',charset='utf8',local_infile=True)
全代码如下:#
注释应该能看懂,有疑问的地方可以留言一起探讨~::quyin:1huaji::
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
'''
@author: soapffz
@fucntion: 批量导入固定字符分割的txt到mysql
@time: 19-04-06
'''
import os # 文本名称获取及cmd命令执行
import pymysql # Python3用pymysql,Python2用mysqldb
from chardet.universaldetector import UniversalDetector # 判断文件编码
import timeit # 计算用时
def create_db():
# 如果数据库不存在则创建,字符集为utf8,排序规则为utf8_general_ci
sql_create_db = "CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS `soendb` default charset utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci;"
# 创建taobao这个表含有两个两个字段mail和passwd
sql_create_table = """
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `taobao` (
`mail` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`passwd` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL
) ENGINE=MyISAM DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
"""
# 自行选择需要创建哪些东西
try:
cursor.execute(sql_create_db)
cursor.execute('use soendb;') # 将当前数据库设置为刚创建的数据库
cursor.execute(sql_create_table)
except Exception as e: # 捕获所有异常并打印,python2 是Exception,e
print("数据库创建出错:{}\n退出程序!".format(e))
connect_mysql.rollback() # 发生错误时回滚
connect_mysql.close() # 关闭数据库连接
exit(0)
def textencoding_lineterminators_modifi(txt_name_list):
# 处理文本编码及字符
processed_txt_filename_list = []
for i in txt_name_list:
detector = UniversalDetector()
print("正在检测{}的文件编码".format(i))
detector.reset() # 清空喂食池
for line in open(i, 'rb').readlines(20000000): # 迭代200W行,足以检测出结果
detector.feed(line) # 喂食
if detector.done: # 如果有结果,退出
break
detector.close()
src_enc = detector.result['encoding']
# 如果编码不为utf-8,则用iconv将xx.txt转换为utf8-xx.txt
if 'utf-8' not in src_enc.lower():
utf8_txt_name = "utf8-{}".format(i)
print("{}不是utf-8编码,正在转换为{}".format(i, utf8_txt_name))
try:
os.popen(
'iconv -c -f {} -t utf-8 {} > {}'.format(src_enc, i, utf8_txt_name))
except Exception as e:
print("转换报错:{} \n 程序退出!".format(e))
exit(0)
processed_txt_filename_list.append(utf8_txt_name)
else:
processed_txt_filename_list.append(i)
return processed_txt_filename_list
def import_txt_to_mysql(txt_name):
# 将txt导入mysql
sql_insert_txt = """
LOAD DATA LOCAL INFILE "{}" INTO TABLE `taobao`
FIELDS TERMINATED BY '----' LINES TERMINATED BY '\r\n';
""".format(txt_name)
# --字段用'----'分隔(例子),记录用CRLF进行分隔(例子)
try:
cursor.execute('use soendb;')
cursor.execute(sql_insert_txt)
# 提交到数据库执行
connect_mysql.commit()
except Exception as e:
print("导入数据出错:{}\n退出程序!".format(e))
connect_mysql.rollback()
connect_mysql.close()
exit(0)
if __name__ == "__main__":
start_time = timeit.default_timer()
# 连接数据库,密码后面可以加数据库名称
try:
connect_mysql = pymysql.connections.Connection(
'localhost', 'root', 'root', charset='utf8', local_infile=True)
# 得到一个可以执行SQL语句的光标对象,执行完毕返回的结果默认以元组显示
cursor = connect_mysql.cursor()
except Exception as e:
print("数据库连接出错 :{}\n退出程序!".format(e))
exit(0)
print("数据库连接成功")
create_db() # 可选,创建数据库及表
# 获取当前目录所有txt文件的文件名
src_txt_filename_list = [filename for filename in os.listdir(
".") if filename.split(".")[-1] == 'txt']
if src_txt_filename_list: # 如果当前目录txt名字列表不为空,则将列表拿去检测编码得到新txt名字列表
processed_txt_filename_list = textencoding_lineterminators_modifi(
src_txt_filename_list)
for txt_name in processed_txt_filename_list:
try:
print("正在导入{}".format(txt_name))
import_txt_to_mysql(txt_name)
except Exception as e:
print("导入数据出错:{}\n退出程序!".format(e))
connect_mysql.rollback()
connect_mysql.close()
exit(0)
else:
print("未获取到txt文件名称,请重新检查!")
end_time = timeit.default_timer()
print("数据库导入完毕,总用时{}".format(end_time-start_time))
效果如下:
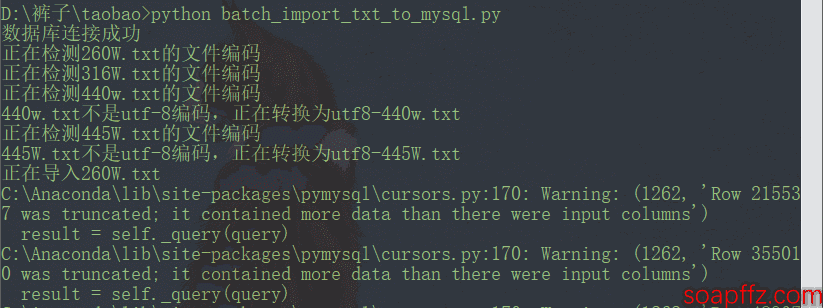
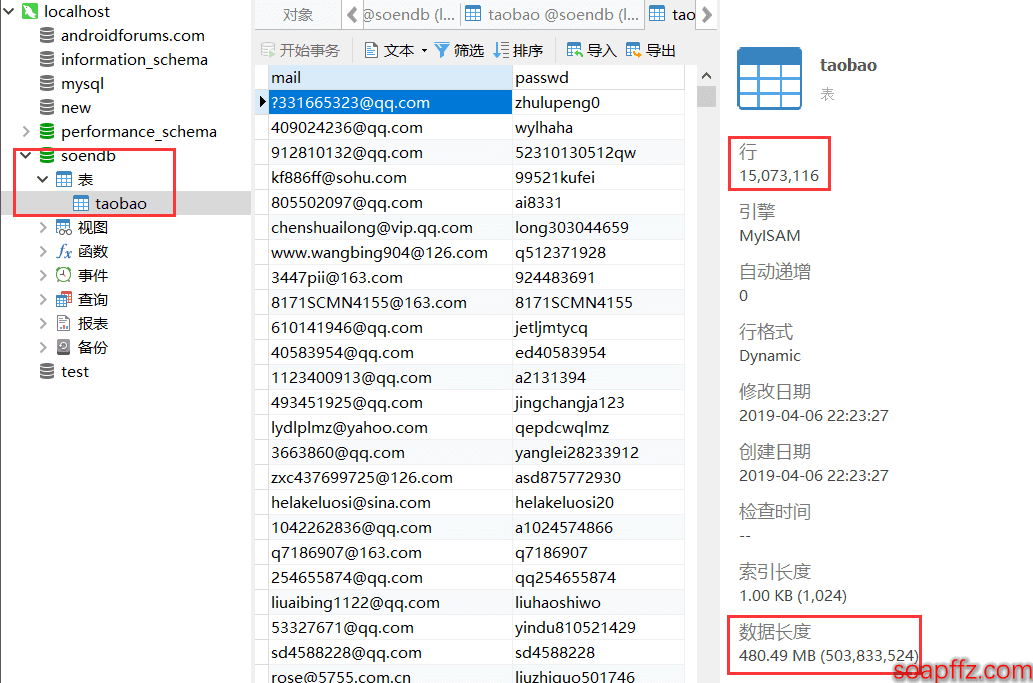
其实 200 多秒,99% 以上的时间都在验证文件的编码,但是就像我文中说的那样,file命令准确性基本只适用于chardet检测可信度为 100% 的编码的文件,其他的基本就是瞎报,但是chardet速度又太慢了,尽管我已经投机取巧设置了 200W 行的上限
当然你也可以不进行验证,所有文件都转换为utf-8编码
所以,有什么好的在Windows下 (如果是Linux也最好能在Windows下找到) 的批量验证并修改文件编码的工具,欢迎大家留言讨论交流~
Notes:
- 加载文件的路径必须是 /,但是 win 复制的默认是 \,文中未处理因为此 py 文件默认是放到 txt 所在目录执行的所以不存在路径问题
- 对于插入、更新、删除等操作,需要使用 connect_mysql.commit () 来提交到数据库执行,对于查询、创建数据库和数据表的操作不需要此语句。
- 其实大部分代码是重复的,但是为了更方便阅读以及防止有些看官用不到某些功能,我这里还是分开写了
参考链接:
- python 实现文本文件的编码检测和转换
- linux 去掉 windows 下文件中的 \r
- Python3 MySQL 数据库连接 - PyMySQL 驱动
- PyMySQL 的基本使用
- PyMYSQL 模块
BreachCompilation#
[19-4-10 更新] 每个都检测编码实在是太费劲了,我在按照安全脉搏的 14 亿泄露数据整理文章整理 Freebuf 等网站发布的数据安全咨询文章14 亿邮箱泄露密码明文信息查询网站惊现网络 时,这里的数据都是这样的:
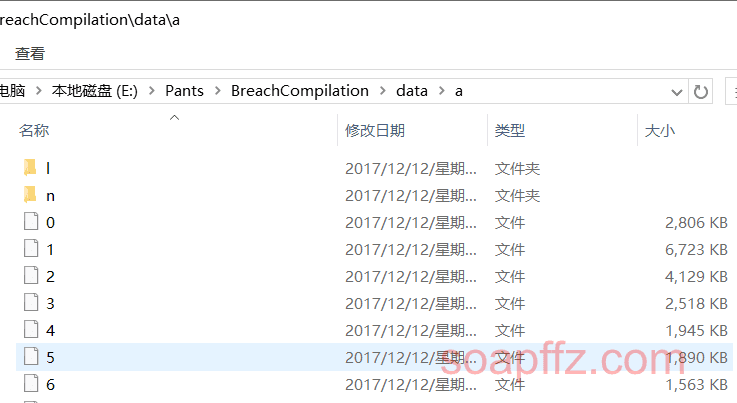
有很多文件夹有子文件,数据文件没有后缀名,我们主要使用cat * > 1.txt这条命令来把他们合并到指定文件夹
代码快写完的时候发现 shell 一条命令就能合并文件夹 (包括子文件夹) 内的所有文件,参考文章
> find . 递归从本文件夹开始查找文件
> -type f 指定文件类型为普通文件,还可以选用的项有:d 目录、l 链接符号、c 字符设备、b 块设备、s 套接字等
> -amin/-mmin/-cmin 可以指定文件的访问时间/修改时间/改变时间。e.g. find . -type f -atime +7 -print 打印出访问时间超过七天的所有文件
> -perm 根据文件权限查找文件
> -user 更具文件所有者查找文件
> -delete 将删除查找到的文件
> -exec 对查找到的文件执行命令,格式为: -exec ./commands.sh {} \;
当时的内心是崩溃的::quyin:hematemesis::,幸好试了下win自带的find命令只能搜索文件中的字符串,而安装的Git即使选了用Unix覆盖win自带的部分指令这个选项,也不能用find, 所以内心又恢复正常::quyin:witty::
文本整理的主要核心命令:进入每个文件夹并执行cat指令,每条指令不阻塞,但是希望多线程并互不干扰
参考文章:Python 执行 cmd 的各种实现方法及优劣(subprocess.Popen, os.system 和 commands.getstatusoutput)
并在这篇文章上补充:
os.system () 这个函数是阻塞的但是不会返回报错信息,每条指令必须执行完才会执行下一条
在 3.x 版本总,commands 库的三个方法之一 getstatus () 方法被移除,getoutput () 和 getstatusoutput () 被放到了 subprocess 模块中。(即 3.x 版本不再使用 commands 库,而是 subprocess 库)
以下为全代码:
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
'''
@author: soapffz
@fucntion: 批量导入固定字符分割的txt到mysql(粗鲁编码转换)
@time: 19-04-11
'''
import os # 文本名称获取及cmd命令执行
import shutil # 文件及目录相关处理
import subprocess # 执行cmd命令
import pymysql # Python3用pymysql,Python2用mysqldb
import timeit # 计算用时
import re # 用正则表达式查找分离文件名
class db_progress:
def __init__(self):
self.collections_dir = 'E:\Pants\BreachCompilation\collections'
self.connect_mysql()
self.create_db()
def connect_mysql(self):
# 连接数据库,密码后面可以加数据库名称
try:
self.mysql_conn = pymysql.connections.Connection(
'localhost', 'root', 'root', charset='utf8', local_infile=True)
# 得到一个可以执行SQL语句的光标对象,执行完毕返回的结果默认以元组显示
self.cursor = self.mysql_conn.cursor()
print("数据库连接成功")
except Exception as e:
print("数据库连接出错 :{}\n退出程序!".format(e))
exit(0)
def create_db(self):
# 如果数据库不存在则创建,字符集为utf8,排序规则为utf8_general_ci
sql_create_db = "CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS `14yi` default charset utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci;"
# 自行选择需要创建哪些东西
try:
self.cursor.execute(sql_create_db)
self.cursor.execute('use 14yi;') # 将当前数据库设置为刚创建的数据库
except Exception as e: # 捕获所有异常并打印,python2 是Exception,e
print("数据库创建出错:{}\n退出程序!".format(e))
self.mysql_conn.rollback() # 发生错误时回滚
self.mysql_conn.close() # 关闭数据库连接
exit(0)
def import_txt_to_mysql(self, txt_name_list):
if not txt_name_list:
# 如果未获取到txt_name_list,则说明文件编码处理失败
print("文件编码可能错误,没有获取到txt名字列表,请重新检查!\n程序退出!")
print(0)
else:
# 将当前工作目录转到collections文件夹
os.chdir(self.collections_dir)
# 将txt导入mysql
for txt_name in txt_name_list:
table_name = re.findall(".*data-(.*).txt", txt_name)[0]
# 创建一个表含有两个两个字段mail和passwd
sql_create_table = """
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `{}` (
`mail` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`passwd` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL
) ENGINE=MyISAM DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
""".format(table_name)
# 将文件插入数据库
sql_insert_txt = """
LOAD DATA LOCAL INFILE "{}" INTO TABLE `{}`
FIELDS TERMINATED BY ':' LINES TERMINATED BY '\n';
""".format(txt_name, table_name)
# --字段用':'分隔(例子),记录用CRLF进行分隔(例子)
try:
print("正在导入{}".format(txt_name))
self.cursor.execute('use 14yi;')
self.cursor.execute(sql_create_table)
self.cursor.execute(sql_insert_txt)
self.mysql_conn.commit() # 提交到数据库执行
except Exception as e:
print("导入数据出错:{}\n退出程序!".format(e))
self.mysql_conn.rollback()
self.mysql_conn.close()
exit(0)
class txt_progress:
def __init__(self):
self.root_dir = 'data'
self.collections_dir = 'E:\Pants\BreachCompilation\collections'
self.utf8_txt_name_list = []
if os.path.exists(self.collections_dir):
# 目录存在则连子文件夹一起删除
shutil.rmtree(self.collections_dir)
os.mkdir(self.collections_dir)
self.txt_collections(self.root_dir)
self.txt_coding_conv()
def txt_collections(self, path):
# 将每个文件夹内的文件用cat命令存到collections_dir文件夹中
for item in os.listdir(path):
subFile = os.path.join(path + "\\" + item)
if os.path.isdir(subFile):
try:
# 用正则表达式查找分离文件名
txt_name = os.path.join(self.collections_dir, re.split(
r'BreachCompilation\\', os.path.abspath(subFile))[-1].replace("\\", '-'))
print("正在转换{}".format(txt_name))
# 进入每个文件夹,将每个文件夹内所有内容合并到collections的对应名字的txt内
cc = 'cd {} && cat * > {}.txt'.format(
os.path.abspath(subFile), txt_name)
subprocess.run(cc, shell=True, stdout=subprocess.PIPE)
except Exception as e:
print("转换报错:{} \n 程序退出!".format(e))
exit(0)
self.txt_collections(subFile)
def txt_coding_conv(self):
os.chdir(self.collections_dir)
# 将collections_dir文件夹中所有文件转换为utf-8编码并返回txt_name_list供insert_txt_to_mysql函数
for item in os.listdir("."):
try:
utf8_txt_name = "utf8{}".format(item) # 新名字
# 强制转换所有txt到utf-8编码
subprocess.run('iconv -c -f ISO-8859-1 -t utf-8 {} > {}'.format(
item, utf8_txt_name), shell=True, stdout=subprocess.PIPE)
self.utf8_txt_name_list.append(utf8_txt_name)
except Exception as e:
print("转换报错:{} \n 程序退出!".format(e))
exit(0)
return self.utf8_txt_name_list
if __name__ == "__main__":
start_time = timeit.default_timer()
progress_db = db_progress()
progress_txt = txt_progress()
# 将转化 后的utf8-_txt_name_list传给导入数据库函数
progress_db.import_txt_to_mysql(progress_txt.utf8_txt_name_list)
end_time = timeit.default_timer()
print("程序执行完毕,总用时{}".format(end_time-start_time))
效果如下:
暂时无效果,还有点小问题
7x7x#
[19-04-13 更新] 有了模板之后,其他固定字符分割的 txt 导入 mysql 的问题就很简单了,用模板改一下就行
这次是某国内游戏网站 7x7x 的数据库 (网上搜集来的):
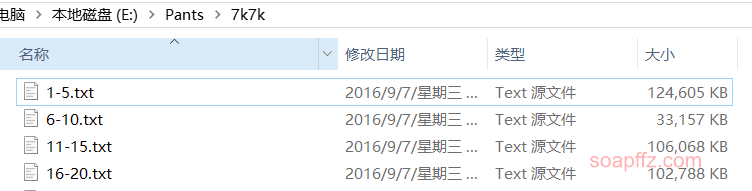
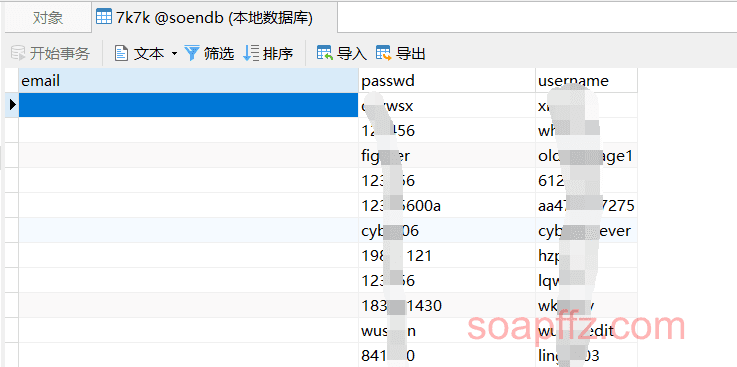
以\t作为分隔符这个数据库的比较特殊的地方在于它是同时有邮箱\t密码和用户名\t密码两种数据存在的:
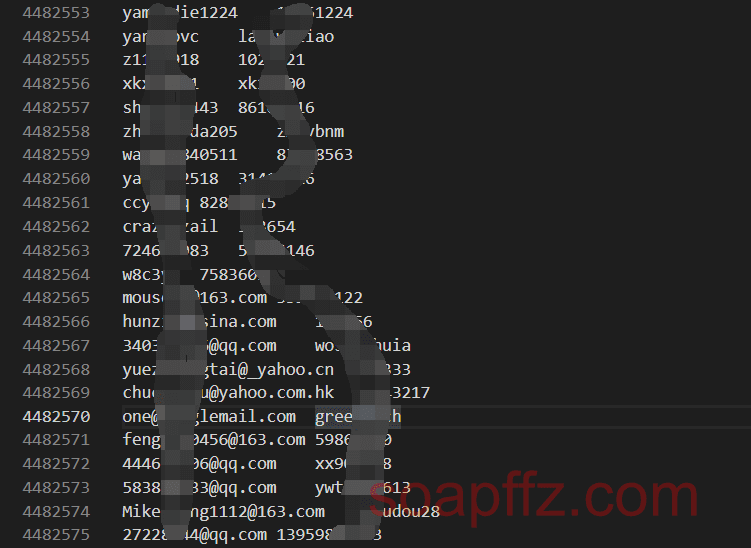
所以创建表的时候就要创建三个字段:email、passwd、username
检测到此行不含@符号 (即不含邮箱时),则拼接为\t密码\t用户名的形式,(因为email-passwd的数据占较大比例所以把username放在最后面)
全代码如下:
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
'''
@author: soapffz
@fucntion: 从7k7k数据库批量导入固定字符分割的txt到mysql(编码转换)
@Comment: 7k7k这几个文本用文本编码精致检测方法检测都是utf-8,故此程序中不添加编码转换
@comment: 但是由于有的是邮箱-密码,有的是用户名-密码,故添加文本整理函数
@time: 19-04-13
'''
import os # 文本名称获取及cmd命令执行
import subprocess
import pymysql # Python3用pymysql,Python2用mysqldb
import timeit # 计算用时
import re # 用正则表达式查找分离文件名
class db_progress(object):
def __init__(self):
self.connect_mysql()
self.create_db()
def connect_mysql(self):
# 连接数据库,密码后面可以加数据库名称
try:
self.mysql_conn = pymysql.connections.Connection(
'localhost', 'root', 'root', charset='utf8', local_infile=True)
# 得到一个可以执行SQL语句的光标对象,执行完毕返回的结果默认以元组显示
self.cursor = self.mysql_conn.cursor()
print("数据库连接成功")
except Exception as e:
print("数据库连接出错 :{}\n退出程序!".format(e))
exit(0)
def create_db(self):
# 如果数据库不存在则创建,字符集为utf8,排序规则为utf8_general_ci
sql_create_db = "CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS `soendb` default charset utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci;"
# 检测表是否存在,存在则删除,然后创建
sql_table_detection = "DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `7k7k`;"
sql_create_table = """
CREATE TABLE `7k7k` (
`email` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`passwd` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`username` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL
) ENGINE=MyISAM DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
"""
try:
self.cursor.execute(sql_create_db)
self.cursor.execute('use soendb;') # 将当前数据库设置为刚创建的数据库
self.cursor.execute(sql_table_detection) # 检测表是否存在,存在则删除,然后创建
self.cursor.execute(sql_create_table)
except Exception as e: # 捕获所有异常并打印,python2 是Exception,e
print("数据库创建出错:{}\n退出程序!".format(e))
self.mysql_conn.rollback() # 发生错误时回滚
self.mysql_conn.close() # 关闭数据库连接
exit(0)
def import_txt_to_mysql(self, txt_name_list):
if not txt_name_list:
# 如果未获取到txt_name_list,则说明文件编码处理失败
print("文件编码可能错误,没有获取到txt名字列表,请重新检查!\n程序退出!")
exit(0)
else:
# 将txt导入mysql
for txt_name in txt_name_list:
sql_insert_txt = """
LOAD DATA LOCAL INFILE "{}" IGNORE INTO TABLE `7k7k`
FIELDS TERMINATED BY '\t' LINES TERMINATED BY '\r\n';
""".format(txt_name)
# --字段用'\t'分隔(例子),记录用LFCR进行分隔(例子)
try:
print("正在导入{}".format(txt_name))
self.cursor.execute('use soendb;')
self.cursor.execute(sql_insert_txt)
self.mysql_conn.commit() # 提交到数据库执行
except Exception as e:
print("导入数据出错:{}\n退出程序!".format(e))
self.mysql_conn.rollback()
self.mysql_conn.close()
exit(0)
class txt_progress:
def __init__(self):
self.processed_txt_filename_list = []
self.txt_process()
def txt_process(self):
# 整理同时含有邮箱-密码和用户名-密码的文本
# 过滤特殊字符
special_characters = ['?', 'ú', 'ü']
for i in os.listdir("."):
if os.path.splitext(i)[1] == ".txt":
print("正在整理{}".format(i))
with open(i, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
processed_txt_name = "processed-{}".format(i)
with open(processed_txt_name, 'a', encoding='utf-8') as k:
for j in f.readlines():
# 删除含有特殊字符的行
if any(chs in j for chs in special_characters):
continue
split = j.split('\t')
# 如果账号不存在或者密码不存在,则删除此行
if '' in split:
continue
# 如果密码中含有中文,则删除此行
if re.compile(u'[\u4e00-\u9fa5]').search(split[-1]):
continue
# 如果用户名不是邮箱,重新排列为:\t密码\t用户名\n
if '@' not in split[0]:
j = '\t' + \
split[-1].strip('\n') + \
'\t' + split[0] + '\n'
k.write(j)
self.processed_txt_filename_list.append(processed_txt_name)
return self.processed_txt_filename_list
if __name__ == "__main__":
start_time = timeit.default_timer()
progress_db = db_progress()
progress_txt = txt_progress()
progress_db.import_txt_to_mysql(progress_txt.processed_txt_filename_list)
end_time = timeit.default_timer()
print("程序执行完毕,总用时{}".format(end_time-start_time))
运行效果如下:
郑重声明: 此文章内分析用到的数据集仅为学习交流,本文未提供任何下载链接且已在 24 小时内删除,请勿用于非法用途否则产生的一切后果自行承担